Highly qualified cardiologists in Singapore use percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, to unblock heart arteries. This treatment improves blood flow to the heart muscle and addresses coronary artery disease. These professionals perform PCI with cutting-edge medical equipment. This article provides a thorough rundown of the procedures involved in coronary angioplasty in Singapore, highlighting important phases and patient considerations.
Initial Assessment and Diagnosis
Before coronary angioplasty, patients typically undergo several diagnostic tests to assess their condition’s severity. These tests include coronary angiography, cardiac screening, and echocardiogram. Coronary angiography in Singapore involves X-ray imaging to visualise the coronary arteries, helping cardiologists identify blockages and determine the appropriate treatment. Cardiac screening in Singapore includes stress tests, ECGs, and blood tests to evaluate overall heart health. An echocardiogram in Singapore uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, providing detailed information about heart function and structure. These diagnostic tests are crucial for planning the angioplasty procedure.
Preparation for the Procedure
After deciding to perform coronary angioplasty, we prepare the patient for the procedure. We provide detailed instructions on pre-procedure preparations, such as fasting and medication adjustments. We admit the patient to the hospital and insert an intravenous (IV) line for administering medications and fluids. The cardiologist explains the procedure to the patient and answers any questions they may have. We obtain informed consent and move the patient to the catheterisation laboratory, where we will perform the angioplasty.
The Angioplasty Procedure
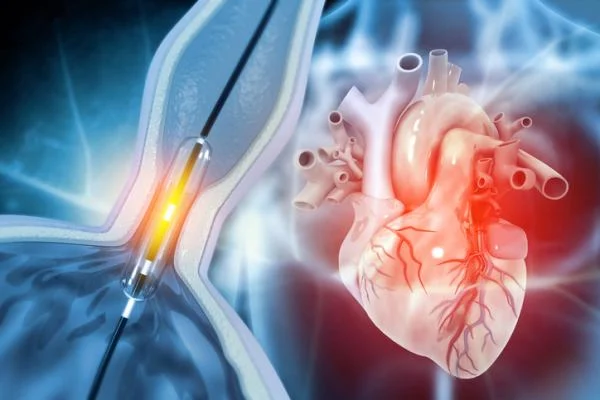
The medical team begins the coronary angioplasty procedure by administering local anaesthesia to numb the area where they will insert the catheter, usually the groyne or wrist. They make a small incision and insert a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the blood vessel. The team carefully guides the catheter through the blood vessels to the coronary arteries, using X-ray imaging for guidance. Once they reach the blockage, they inflate a balloon attached to the tip of the catheter. This balloon presses the plaque against the artery walls, opening the artery and restoring blood flow. They place a stent (a small wire mesh tube) in the artery to keep it open. This procedure is known as heart stenting treatment and is a common component of coronary angioplasty in Singapore. The stent remains in the artery permanently, providing ongoing support to the blood vessel.
Post-Procedure Care and Monitoring
After the procedure, the patient is moved to a recovery area where they are closely monitored for complications. The catheter insertion site is checked for bleeding or swelling, and vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure are regularly monitored. The patient may lie flat for several hours to prevent bleeding from the catheter insertion site. Pain at the insertion site is managed with medications, and the patient is encouraged to drink fluids to help flush out the contrast dye used during the procedure. Most patients can return home within 24 to 48 hours after the procedure, but this may vary depending on individual health conditions and the complexity of the procedure.
Follow-up and Long-Term Care
Successful recovery from coronary angioplasty involves careful follow-up and lifestyle modifications. Patients are typically scheduled for follow-up appointments with their cardiologist to monitor their progress and manage potential complications. Medications to prevent blood clots, lower cholesterol, and control blood pressure are usually prescribed. Patients are advised to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation. Regular heart screening in Singapore is recommended to monitor heart health and detect any recurrent issues early. Cardiac rehabilitation programs may also be suggested to help patients regain strength and improve cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Coronary angioplasty in Singapore is a well-established procedure using state-of-the-art technology. The process involves thorough diagnostic assessments, careful preparation, precise execution, and diligent post-procedure care. By following their cardiologist’s recommendations and making necessary lifestyle changes, patients can achieve optimal outcomes and significantly improve their heart health.
Contact Dr Leslie Tay today for more information.

